Purchase Order Process – Everything you need to know
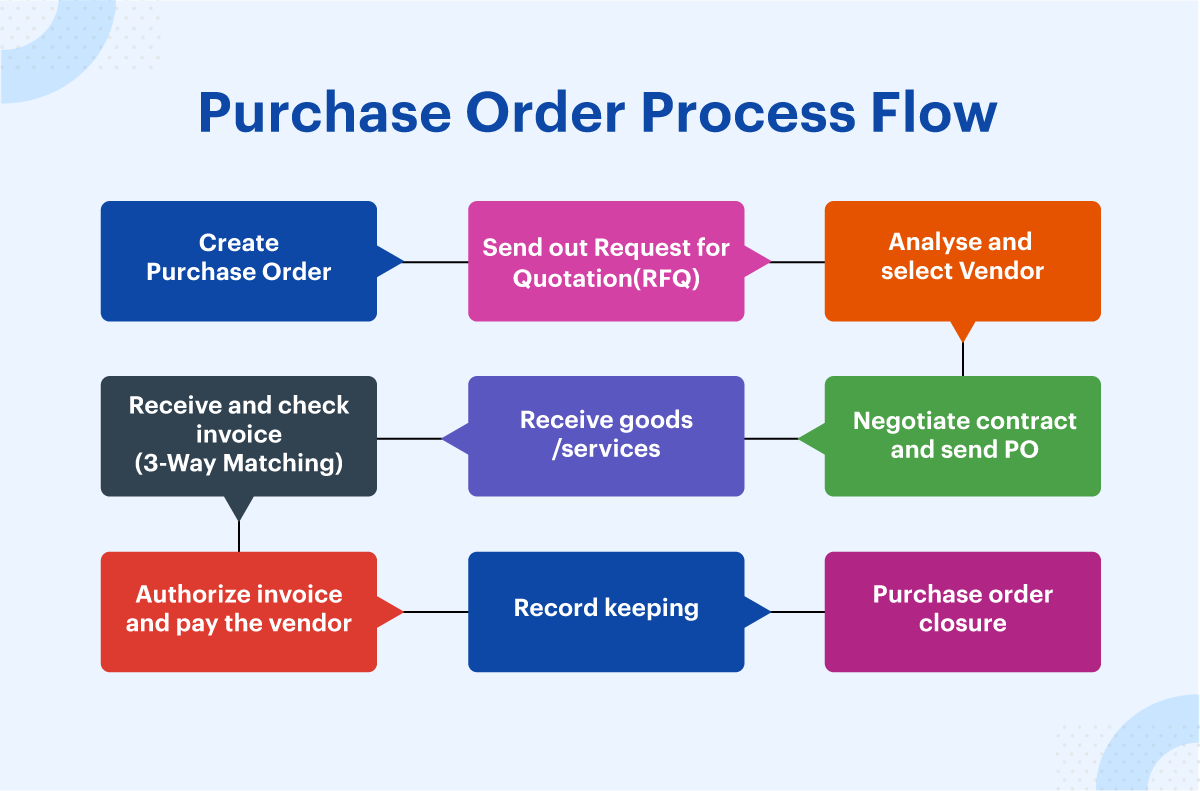
Purchase order process flow
The purchase order process consists of several compliance checkpoints and approval/input tasks to ensure timely PO processing. Here are the most common purchase order process steps:
- Create a purchase order
- Send out multiple requests for quotation(RFQ)
- Analyze and select a vendor
- Negotiate contract and send PO
- Receive goods/services
- Receive and check invoice (3-Way Matching)
- Authorize invoice and pay the vendor
- Record keeping
- Purchase order closure
Where Do Purchase Orders Fit Into the Purchase-to-Pay Process?
Purchase orders are a critical component within the broader purchase-to-pay (P2P) process, as they provide control once a purchase has been approved.
An effective purchase-to-pay process helps to streamline and optimize procurement, ensuring that purchases align with budgetary constraints, organizational policies, and compliance requirements while fostering efficient communication between your organization and your vendors.
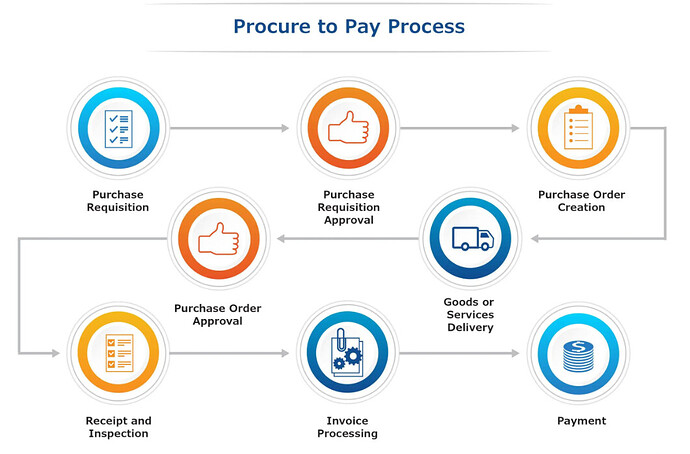
Here’s a step-by-step overview of the purchase-to-pay process, including where purchase orders fit in.
Step 1: Purchase Requisition
The P2P process typically begins when someone in the business (the Purchaser) identifies a need for a good or service and submits a purchase requisition (PR) to initiate the process. The PR is an internal document outlining the requested items’ requirements, specifications, and estimated costs. In cases where the Purchaser has already selected a vendor, the PR will collect information on the vendor, along with documentation of any bids or quotes the vendor has already provided.
Step 2: Purchase Requisition Approval
The purchase requisition is then routed for approval based on predefined approval authority. The approver will review the request and any supporting documentation, such as formal bids or quotes, to ensure the goods or services are needed and within budget.
Step 3: Purchase Order Creation
The purchasing department (or relevant personnel) create the purchase order based on the approved purchase requisition. The PO is an external document sent to the vendor to authorize the provision of the requested goods or services.
Step 4: Purchase Order Approval
The purchase order typically requires approval from authorized personnel, such as department heads or procurement managers, to ensure it aligns with budgetary constraints and organizational policies. Once approved, the PO is sent to the vendor to initiate the transaction formally.
Step 5: Goods or Services Delivery
Upon accepting the purchase order, the vendor prepares and delivers the specified goods or services within the agreed-upon time frame.
Step 6: Receipt and Inspection
The purchaser (or receiving department) checks the delivered items against the details in the purchase order to verify the quantity, quality, and condition. Any discrepancies are documented and remediated.
Step 7: Invoice Processing
Once the goods or services are received and accepted, the vendor sends an invoice, typically referencing the purchase order number. The invoice matches the purchase order (and the receiving report, when applicable), ensuring all details align.
Step 8: Payment
After the invoice is verified and matched, payment is authorized and sent to the vendor using the agreed-upon payment method, such as check, ACH, wire, or virtual card.